DAT Reactions I • DAT Reactions II • DAT Reactions III • Substitution vs Elimination • Official Topics • GS ORG Review
Our Gold Standard DAT Organic Chemistry Reactions and Summary page is not intended to be an exhaustive ORG review. That requires much more than one page. However, we hope you find a helpful summary of key organic chemistry reactions to help make your DAT review a bit easier. Consider printing the reactions and reviewing the logic frequently. As much as possible, try to make sense of the reactions and avoid memorizing. You will notice reactions that are numbered and then described below. If you happen to have the Gold Standard DAT Chemistry book, we have placed the cross-reference to the section of the book for more information regarding any reaction or mechanism (i.e. ORG 4.2 = Organic Chemistry chapter 4, section 4.2).
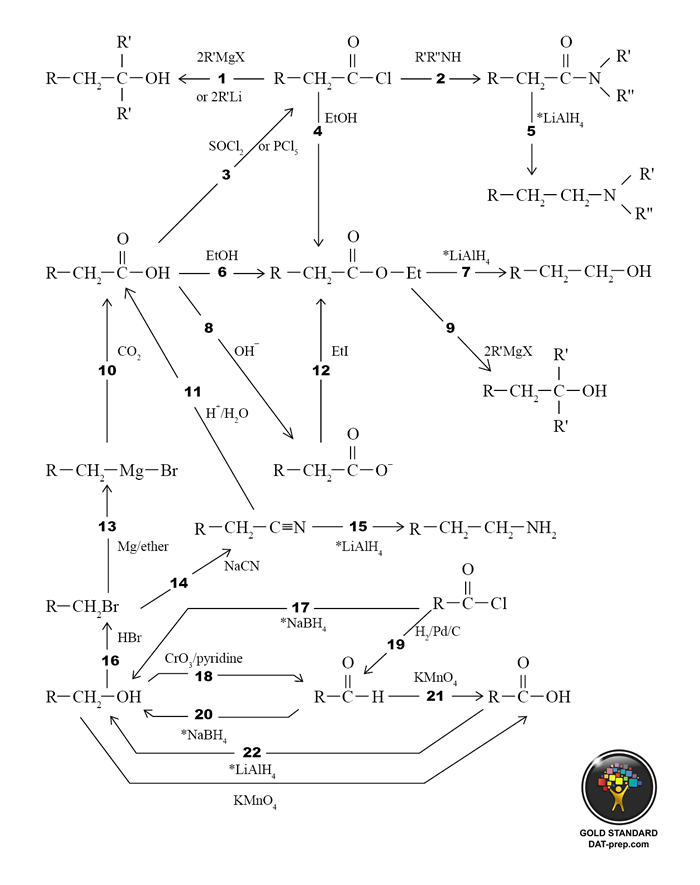
DAT Organic Chemistry Reactions: Summary I
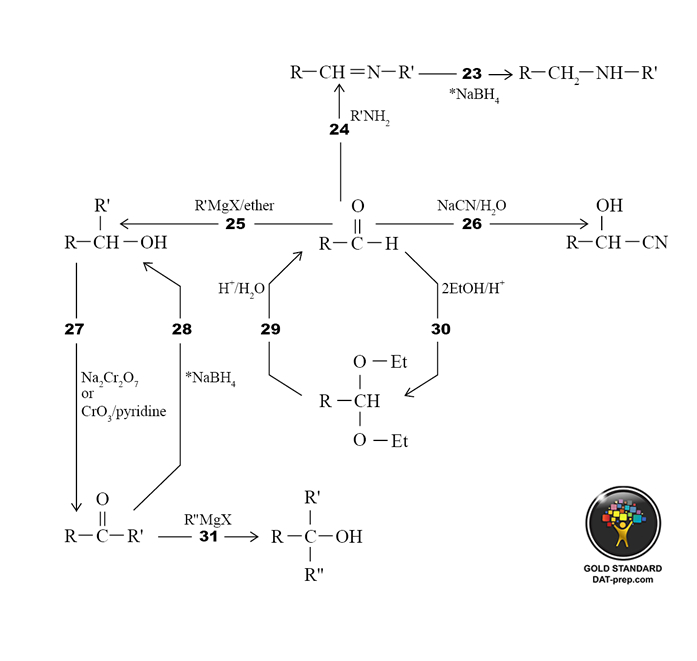
DAT Organic Chemistry Reactions: Summary II
DAT Organic Chemistry Reactions: Summary III
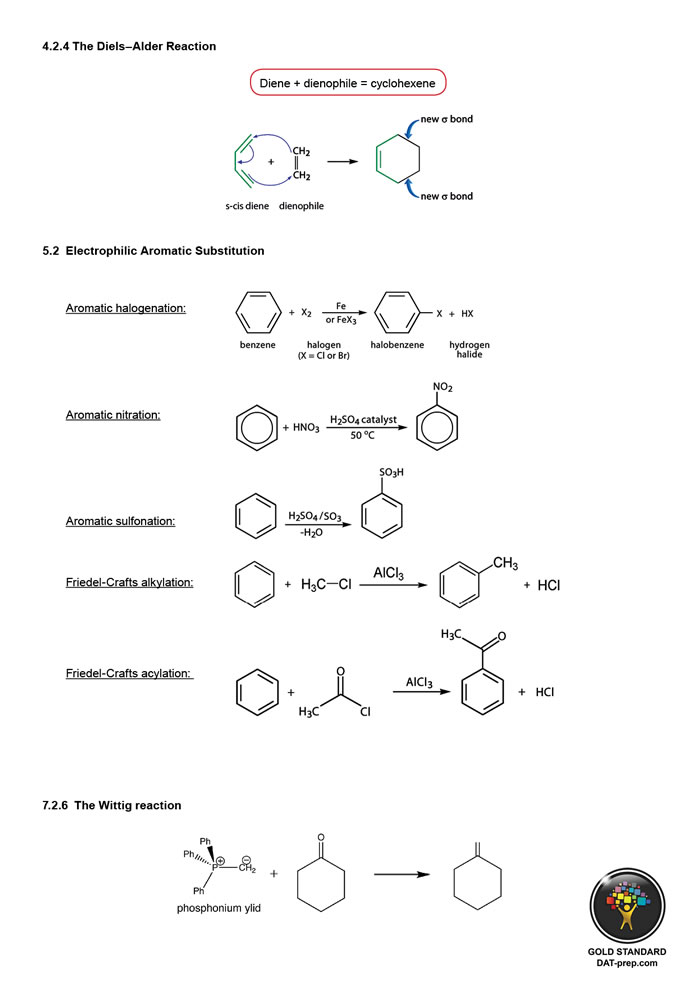
R = alkyl
Et = ethyl
X = halide
R-MgX+ = grignard reagent
R-Li+ = alkyl lithium
Grignard reagents and alkyl lithiums are special agents since they can create new C—C bonds.
*Reduction = addition of hydrogen or subtraction of oxygen. Mild reducing agents add fewer hydrogens/subtract fewer oxygens. Strong reducing agents add more hydrogens/subtract more oxygens. Cross-referencing to The Gold Standard DAT text.
Most reactions presented can be derived from basic principles (i.e. ORG 1.6, 7.1).
- An acid chloride reacts with a grignard reagent to produce a tertiary alcohol. See ORG 9.1
- An acid chloride reacts with a primary or secondary amine to produce an amide. See ORG 9.3 & 11.2.
- A carboxylic acid reacts with SOCl2 or PCl5 to produce an acid chloride. See ORG 9.1.
- An acid chloride reacts with an alcohol (e.g. ethanol) to produce an ester. See ORG 9.4.
- An amide reacts with LiAlH4 to produce an amine. See ORG 8.2, 9.3.
- A carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol (e.g. ethanol) to produce an ester. See ORG 8.2.
- An ester reacts with LiAlH4 to produce a primary alcohol. See ORG 8.2, 9.4.
- A carboxylic acid reacts with base to produce a carboxylate anion. See CHM 6.3 & ORG 8.1.
- An ester reacts with a grignard reagent to produce a tertiary alcohol. See ORG 9.4.
- A grignard reagent reacts with carbon dioxide to produce a carboxylic acid. See ORG 8.1.1.
- A nitrile reacts with aqueous acid to produce a carboxylic acid. Compare to ORG 10.1.1.
- A carboxylate ion reacts with ethyl iodide to produce an ester. Compare to ORG 10.1.1.
- An alkyl halide reacts with Mg/ether to produce a grignard reagent. Compare to ORG 10.1.1.
- An alkyl halide reacts with NaCN to produce a nitrile. See ORG 6.2.3.
- A nitrile reacts with LiAlH4 to produce an amine. See ORG 8.2.
- A primary alcohol reacts with HBr to produce an alkyl halide. Compare to ORG 10.1.1.
- An acid chloride reacts with NaBH4 to produce a primary alcohol. See ORG 8.2, 9.1.
- A primary alcohol reacts with CrO3/pyridine to produce an aldehyde. See ORG 6.2.2.
- A acid chloride reacts with H2/Pd/C to produce an aldehyde. See ORG 7.1 & 9.1.
- An aldehyde reacts with NaBH4 to produce a primary or secondary alcohol. See ORG 7.1, 8.2.
- An aldehyde reacts with KMnO4 to produce a carboxylic acid. See ORG 7.2.1.
- A carboxylic acid reacts with LiAlH4 to produce a primary alcohol. See ORG 8.2.
- An imine reacts with NaBH4 to produce a secondary amine. See 7.2.3, 8.2.
- An aldehyde reacts with a primary amine to produce an imine. See ORG 7.2.3.
- An aldehyde reacts with a grignard reagent and ether to produce a secondary alcohol. See ORG 7.1.
- An aldehyde reacts with aqueous NaCN. See ORG 7.1.
- A secondary alcohol reacts with Na2CrO7 or CrO3/pyridine to produce a ketone. See ORG 6.2.2.
- A ketone reacts with NaBH4 to produce a secondary alcohol. See ORG 7.2.1.
- An acetal reacts with aqueous acid to produce an aldehyde. See ORG 7.2.2.
- An aldehyde reacts with an alcohol (e.g. ethanol) and acid to produce an acetal. Note that using with less EtOH/H+, a hemiacetal will form. See ORG 7.2.2.
- A ketone reacts with a grignard reagent to produce a tertiary alcohol. See ORG 9.1.
Official ADA Organic Chemistry Topic List
- Mechanisms: Energetics, and Structure - elimination, addition, free radical, substitution mechanisms, etc.
- Chemical and Physical Properties of Molecules - spectroscopy (1H-NMR , 13C-NMR, infrared, and multi-spectra), structure (polarity, intermolecular forces, solubility, melting/boiling point, etc.), and laboratory theory and techniques (i.e. TLC, separations, etc.).
- Stereochemistry (structure evaluation) - chirality, isomer relationships, and conformations.
- Nomenclature - IUPAC rules and functional groups in molecules.
- Individual Reactions of the Major Functional Groups and Combinations of Reactions to Synthesize Compounds - alkene/alkyne, aromatic, substitution/elimination, aldehyde/ketone, carboxylic acids and derivatives, and other. For each area of the preceding, the following specifications apply: general, one-step, and multi-step synthesis.
- Acid-Base Chemistry - ranking acidity/basicity (structure analysis and pH/pKa data analysis), and prediction of products and equilibria.
- Aromatics and Bonding - concept of aromaticity, resonance, atomic/molecular orbitals, hybridization, and bond angles/lengths.
Gold Standard Organic Chemistry Review
- Title: DAT Organic Chemistry Masters Series, Review, Preparation and Practice for the Dental Admission Test by Gold Standard DAT
- SRP: $49.95
- Format: Paperback book or eBook
- Pages: 440 pages
- Edition: 2
- ISBN: 978-1-927338-63-6
- Publisher: RuveneCo Inc.
- Authors: DAT-prep.com, Gold Standard DAT
- Series: Book 3 of 6
- Description: Comprehensive chemistry review in color from the atom to thermodynamics to reaction mechanisms to NMR; General Chemistry Equation List & Organic Reaction Summary. Chapters begin with learning objectives and finish with practice multiple choice questions followed by useful explanations. This book also contains the content covering OAT Organic Chemistry.
- Paperback book
- PRICE: $44.95
$49.95
Instant online access available as you await for the book to arrive.
- Online eBook access for 6 months
- PRICE: $24.95
The eBook is 100% online and includes all paperback book features.
Can't I use MCAT books instead?
There are many important DAT General and Organic Chemistry topics that are either not on the MCAT or are so rare as MCAT questions that the topics are not properly covered in MCAT books. Here is a partial list: general chemistry laboratory techniques and glassware, alkene, alkyne, ether and aromatic chemistry, multi-step organic syntheses, etc. The Gold Standard DAT was designed specifically for the DAT so all ADA topics are presented in color followed by chapter review questions, answers and explanations.
Table of Contents for Organic Chemistry
- Molecular Structure of Organic Compounds
- Stereochemistry
- Alkanes
- Alkenes
- Aromatics
- Alcohols
- Aldehydes and Ketones
- Carboxylic Acids
- Carboxylic Acids Derivatives
- Ethers and Phenols
- Amines
- Biological Molecules
- Separations and Purifications
- Spectroscopy
Key Organic Chemistry Reaction Mechanisms
Official ADA DAT Organic Chemistry Test Content (30 questions)
-
Mechanisms:
Energetics, and Structure - elimination, addition, free radical, substitution mechanisms, and other mechanisms and reactions.
-
Chemical and Physical Properties of Molecules:
Spectroscopy (1H NMR, 13C NMR, infrared, and multi-spectra), structure (polarity, intermolecular forces (solubility, melting/ boiling point, etc.), and laboratory theory and techniques (TLC, separations, etc.)
-
Stereochemistry (structure evaluation):
Chirality, isomer relationships, and conformations
-
Nomenclature:
IUPAC rules and functional groups in molecules
-
Individual Reactions of the Major Functional Groups and Combinations of Reactions to Synthesize Compounds:
Fertilization, descriptive embryology, developmental mechanisms.
-
Genetics:
Alkene/alkyne, aromatic, substitution/elimination, aldehyde/ketone, carboxylic acids and derivatives, and other. For each area listed above, the following sub-areas apply: general, one-step, and multi-step.
-
Acid-Base Chemistry:
Ranking acidity/ basicity (structure analysis and pH/ pKa data analysis), and prediction of products and equilibria
-
Aromatics and Bonding:
Concept of aromaticity, resonance, atomic/ molecular orbitals, hybridization, and bond angles/lengths.
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY VIDEO INDEX
-
DISC 1:
- Stereochemistry I
- Stereochemistry II
- Stereochemistry III
- Reaction Mechanisms I
- Reaction Mechanisms II
- Reaction Mechanisms III
- The Carbonyl Group I
- The Carbonyl Group II
-
DISC 2:
- The Carbonyl Group III
- Acetals/Ketals I
- Acetals/Ketals II
- Substitution I
- Substitution II
- Substitution III
- Carboxylic Acids I
- Carboxylic Acids II
-
DISC 3:
- The Tetrahedryl Intermediate
- Amides Amino Acids
- Protein Structure
- Elimination I
- Elimination II
- Alkenes I
- Free Radicals
- Redox Reactions
-
DISC 4:
- Redox Reactions II
- Redox Reactions III
- Aromatic Rings I
- Aromatic Rings II
- Spectroscopy
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
- Elimination vs. Substitution
In addition to the Dental Admission Test guides and software that we recommend to you, please consider visiting the official website for the Dental Admissions Test: click on DAT in the US or click here: DAT for students in Canada. Note: only the Canadian DAT includes manual dexterity/soap carving which is only covered in programs that specifically say so like the Canadian Edition of TopScore Pro.
Copyright © DAT Prep by Gold Standard - RuveneCo, The Only Prep You Need, The Gold Standard and The DAT Prep Bookstore may be either trademarks/service marks or registered trademarks/service marks of RuveneCo Inc. DAT or Dental Admission Test is administered by the ADA or American Dental Association which is not associated with our products. See ADA.org. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction without permission is illegal. These organic chemistry mechanisms and summaries are reproduced with permission from The Gold Standard DAT Chemistry book.